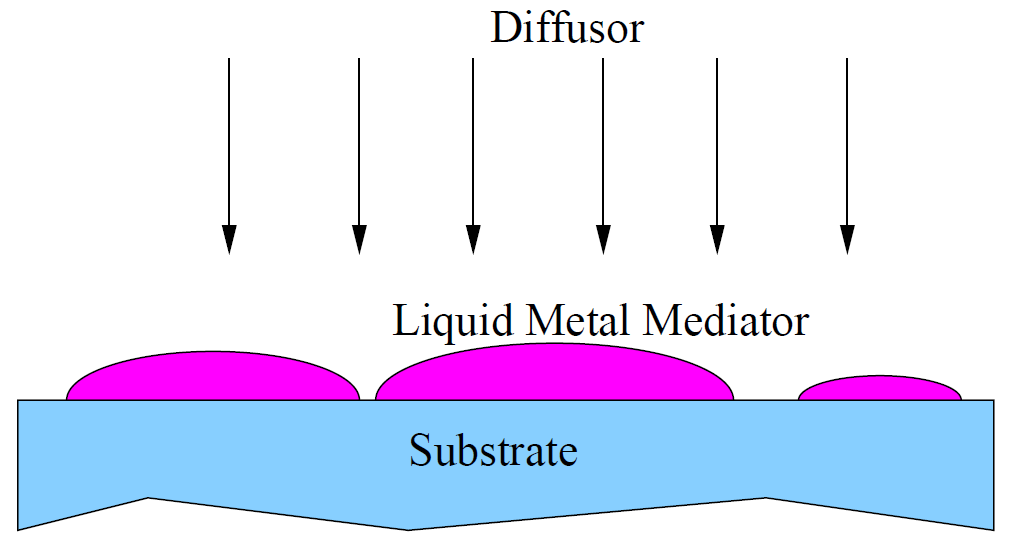
The earliest known predecessor of SMME is liquid metal mediated (LMM) epitaxy[1][2] in which epitaxial growth of c-Si at a buried interface using liquid gold (Au) as a mediator for the deposited Si was reported. Due to a lack of substrate cleaning methods and impure Si sources, the growth of Si whiskers was observed.
With improved vacuum equipment and substrate cleaning methods, Ge diffused through a liquid Au mediator grew homoepitaxially at the buried Ge/Au interface after 20 minutes of annealing Figure 2.1.[3]
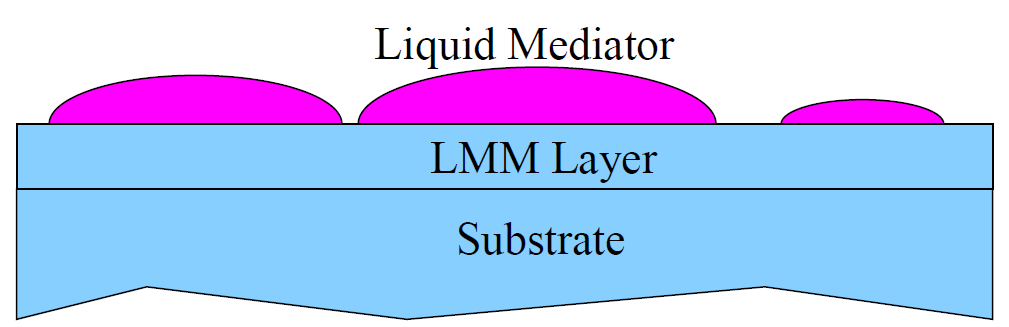
Figure 2-1. Liquid Metal Mediated (LMM) Epitaxy. a) A molecular beam of diffusors is deposited atop a liquid layer of metal mediator. b) The product of LMM is a substrate/LMM film/liquid mediator sandwich. The resulting structure requires an annealing stage to improve the quality of the buried LMM layer. |
SMME requires no additional stages of annealing, and the mediator can be reused for subsequent deposition stages, or incorporated as part of the final device structure.
References
- , “Vapor-Liquid Solid Mechanism of Single Crystal Growth”, Appl. Phys. Lett, vol. 4, 1964.
- , “Trans. Metall. Soc, A. I. M. E.”, Trans. Metall. Soc., vol. 233, 1965.
- , “Liquid Metal Mediated Homoepitaxial Film Growth of Ge at Low Temperature”, Appl. Phys. Lett, vol. 59, 1991.